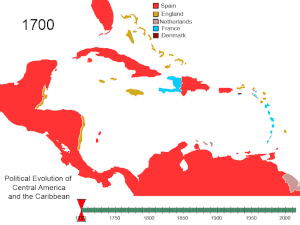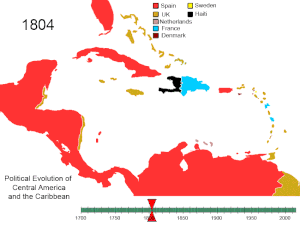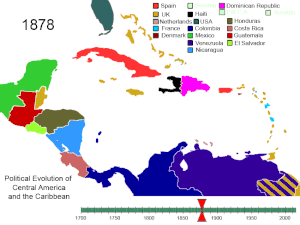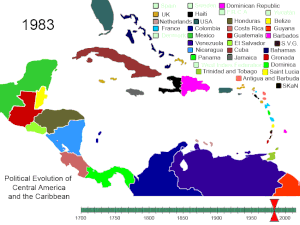
European
rivalry in the Caribbean up to 1763
EUROPEAN SETTLEMENT IN THE AMERICAS UP TO 1763
With Spain facing such growing hostility in the
region, she employed several strategies to protect her American empire. These
included:
a) the use of a convoy system. b) the establishment
of the House of Trade.
c) the utilization of the guarda costa.
d) the fortification of important towns.
e) monopoly port system.
MEASURES USED BY SPAIN TO PROTECT HER EMPIRE IN THE AMERICAS
Spain employed several strategies to protect her
empire. These included:
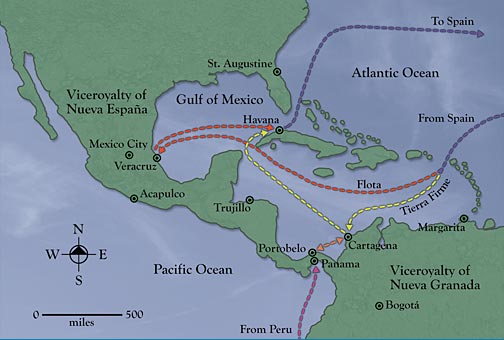
1. THE USE OF A CONVOY SYSTEM
This was a collection of merchant ships with an
escort of warships. This was introduced to reduce the likelihood of privateers
and buccaneers attacking Spanish vessels.
2. THE ESTABLISHMENT OF THE HOUSE OF TRADE
The House of Trade, or Casa de Contratacíon, was a
government agency from the 16th to 18th century which was mandated to control
Spanish exploration and colonization. The body had several functions:
- collecting all taxes and duties.
- licensing captains.
- maintaining secret information on trade routes and new discoveries.
- issuing trade licences (one such was the asiento).
- approving all voyages of exploration and trade.
By controlling the economic framework of the
colonies, Spain assumed it would be easier to maintain its influence over the
colonies.
3. UTILIZATION OF THE GUARDA COSTA
These were coast guards that patrolled the waters
against smugglers and other marauders.
4. THE FORTIFICATION OF IMPORTANT PORTS
This would reduce the likelihood of attacks on
their trading system by rival European nations. Fortified ports existed in
Santo Domingo, Havana, Hispaniola and San Juan in the Caribbean. There was also
the fortification of Cartagena – the guardian of northern South America and
approaches to the Isthmus of Panama.
5. MONOPOLY PORT SYSTEM
Spain ensured that only legally authorised ports
could conduct trade with the settlers in the American empire.
BREAKING OF SPAIN’S AMERICAN EMPIRE
Although Spain tried immensely to safeguard her
control of territories in the Americas, the tactics employed by several
European countries proved successful in destroying her control. These measures
included:
a) illegal trading
b) privateering
c) settlement of several islands in the region.
1. ILLEGAL TRADING
Spain sought to prevent Spanish settlers from
purchasing goods from other European settlers. Oftentimes, Spanish settlers had
to wait until the fleet from Seville returned for them to access items. This
led to shortages in the colonies. Traders such as the English illegally sold
goods such as wine, oil, tools and textiles to the Spanish settlers. By the end
of the 17th century, it was the Dutch who were the busiest illegal traders in
the region and undermining Spain’s economic stronghold over the region.
2. PRIVATEERING
Somali Pirates
Privateers were issued with Letters of Marque –
special papers given by their home government granting permission to attack,
take by force and return the goods from enemy merchant ships. Please note that
buccaneers were not under the directive of any home government. In essence,
they were pirates without licences. However, their efforts were just as
effective as they plundered Spanish ships.
3. SETTLEMENT
The French and English established settlements as a means of containing
Spanish dominance in the Caribbean. They settled on islands that were
considered ‘insignificant’ by the Spanish. By doing so, rival European nations
created a presence in the region and had bases in the area from which to attack
and undermine Spain’s economic stronghold in the Americas. The end result was
that by 1763 Spain’s hegemony in the Americas was reduced significantly.
Class PowerPoint Presentation